The Satellite LNB (Low Noise Block Downconverters) plays a vital role in the complex satellite TV reception and distribution system that delivers a wide variety of TV programmes to viewers around the world who use satellite TV.
What is the satellite LNB on a satellite dish?
The satellite LNB is a receiving device mounted on a satellite dish, responsible for receiving satellite signals and converting them into signals that are then transmitted via coaxial cable to a receiver inside a building.
Therefore, LNB is called the “front end” of satellite reception, and its performance directly affects the image quality and signal stability of satellite TV.
From the point of view of the working principle, an LNB is a device integrating a low noise amplifier, mixer, local oscillator and intermediate frequency (IF) amplifier. It receives satellite microwave signals from a satellite dish and enables signal processing and transmission by amplifying the TV signal and converting the frequency to a lower intermediate frequency block (IF).
This frequency conversion allows the use of a lower-cost coaxial cable to transmit television signals to an indoor satellite television receiver, rather than using expensive and impractical waveguide wires to transmit signals at the original microwave frequency.
How many types of satellite LNBs are there?
According to the demand for satellite TV reception in different scenarios, various types of satellite LNBs have appeared in the global market, and many users don’t know how to choose. This article focuses on the input and output requirements of LNBs to give you a simple and clear understanding of common satellite LNB classifications.
Most satellite LNBs only support receiving all TV signals (V/L, V/H, H/L & H/H) from one satellite, that is, they can only accurately locate one position, which we also call single-feeder. Such single-feeder LNBs are of the following types:
Twin LNB:
It has 2 identical and independent output ports, each capable of providing all satellite TV signals from this satellite to 2 receivers. You can think of these two output ports as a pair of identical twins, everything is the same.
Dual LNB:
There are 2 output ports, each outputting a quarter of the vertical or horizontal signal (V/L, V/H) from this satellite.
It is the type of LNB that was once designed specifically for satellite multiswitch distribution systems. However, very few vendors offer this dual LNB today because it is only for satellite multiswitch systems and has a small range of uses. At the same time, more and more satellite multiswitches nowadays can be adapted to the universal version of the twin LNB, so there is no need to adapt the dual LNB, and it is gradually disappearing from the market. Nowadays, people talk about dual LNB as generally equivalent to twin LNB.
Quad LNB:
It receives TV signals from one satellite and has 4 identical and independent output ports. It can provide all TV signals from this satellite to 4 receivers. You can think of it as identical quadruplets, with no difference among the 4 ports.
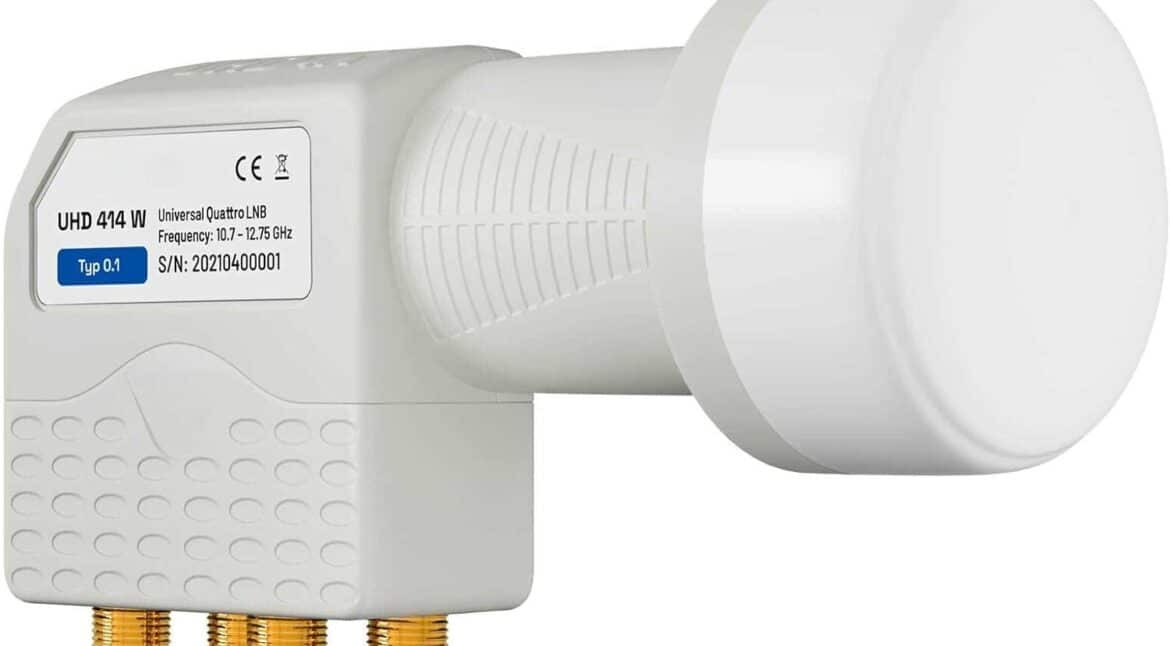
Quattro LNB:
This is a system LNB specially designed for satellite multiswitch systems (or SMATV). Although the Quattro LNB has the same 4 output ports as the Quad LNB, there is a fundamental difference between the two. Each port of the Quattro LNB receives only one-quarter of the TV signals from this satellite, while each port of the Quad LNB receives the full TV signal from this satellite.
Octo LNB:
Similar to Quad LNBs, but with 8 identical and independent output ports, it can provide all TV signals from this satellite to 8 receivers.
Few satellite LNBs support reception of all TV signals (V/L, V/H, H/L and H/H) from two satellites, i.e. they can locate 2 positions, which we can call dual-feeder LNBs:
Monoblock LNB:
Due to the demand for receiving 2 or more satellite signals in some regional countries, a type called Monoblock LNB has appeared in the market. This type of LNB can support receiving TV signals on multiple satellites and can locate 2 satellite positions, we can call it multi-feeder. What looks like one LNB from the outside is 2 LNBs mounted in a single housing, you can think of it as a pair of Siamese twins born from different eggs.
An example blow is this monoblock LNB from Inverto company, which receives all satellite TV signals from two satellites at the same time, 13°E and 16°E.